Easy $130 Bounty: From User to Admin - The Hidden Power of Role Parameter Injection
How a simple profile update turned into an admin-level privilege escalation - and how you can test, prevent, and understand Broken Access Control vulnerabilities ethically.
Disclaimer: This content is for educational and defensive purposes only. All techniques and payloads described are shared to help developers and ethical hackers understand and prevent Broken Access Control vulnerabilities. Never test live systems without authorization or scope approval.
Introduction: The “Too Easy” $130 Bug That Shocked a Hunter
Sometimes, the simplest vulnerabilities hide in plain sight.
This $130 bounty didn’t require advanced exploitation, complex tools, or multi-stage chains. It required curiosity, a keen eye, and a single misplaced parameter.
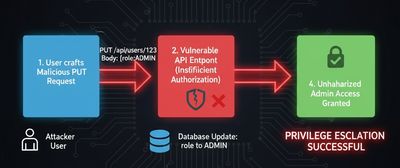
This real-world case demonstrates how a Broken Access Control (BAC) flaw allowed a regular user to become an administrator, simply by injecting "role": "ADMIN" into an API request.
The vulnerability wasn’t flashy - no SQLi, no XSS, no RCE - yet the impact was critical: full administrative access.
The Hunter’s Mindset: Always Observing, Always Testing
The researcher described their approach perfectly:
“When I’m watching YouTube or a movie, my terminal is fuzzing. If I see a site acting differently, that’s another hour added to my night.”
That’s the essence of good hunting - constant observation. Most hunters move on after a quick look. This one didn’t.
One night, while watching a movie, they stumbled upon a movie review site. Curiosity kicked in. Within minutes, they were analyzing registration, login, and profile update flows - core functions that many developers overlook after initial testing.
And that’s where the magic happened.
Step 1 - Register and Observe the Basics
The first step was routine: creating a new account.
The registration request looked like this:
Upon success, the API responded with:
That “role” field instantly drew attention. Why?
Because client-side parameters often hint at deeper backend logic.
The hunter’s first thought:
“Can I manipulate this? Can I become ADMIN?”
Step 2 - The First Attempt: Registration with Injected Role
They re-sent the registration request - this time adding a new JSON key.
No error.
The response was again 201 Created. Promising.
But upon logging in, the dashboard still showed a regular user account.
At this point, most hunters would stop - assuming the system ignored the injected key. But not this one.
They decided to check every endpoint that handled user updates.
Step 3 - Updating the Profile: The Hidden Backdoor
Next stop: Profile Update API.
The typical request looked like this:
This was the perfect place to test privilege-related fields.
So, the researcher injected:
They hit “Send” - expecting an error.
Instead, the response came back clean:
The account was now an administrator.
No bypasses. No encryption. No special tricks - just a missing backend validation.
Moments later, all admin functions were available: viewing all users, moderating content, even managing platform settings.
The Root Cause: Missing Server-Side Authorization Checks
This vulnerability happened because the backend trusted client input instead of validating it.
Here’s what the flawed logic looked like conceptually:
A secure implementation should filter or ignore restricted attributes like “role”:
In short:
Never trust user-controlled parameters for sensitive attributes.
Validation and authorization belong on the server side, not the client.
Step 4 - Reporting Responsibly
The hunter knew the bug was serious - but the site wasn’t part of a formal bug bounty program.
Instead of exploiting the issue, they found contact details for the administrators and reported it ethically via email.
The report included:
- Vulnerability summary
- Proof-of-concept steps
- Screenshots of requests and responses
- Recommendation to sanitize and validate API input
A few days later, they received a humble yet appreciative reply:
“We are very grateful for your help. We have a small budget but want to thank you for your responsible disclosure. Please send your payment details.”
A few days later - $130 paid.
No public program, no triage portal, just pure ethical hacking.
Step 5 - Why This Bug Was So Dangerous
While it sounds simple, role manipulation via JSON injection can have massive consequences.
Possible Impacts:
- Privilege Escalation - A normal user becomes an admin or superuser.
- Data Exposure - Admin panels often grant access to user PII, logs, or payment info.
- Configuration Tampering - Attackers can change system settings or API keys.
- Service Disruption - Malicious users could delete or alter critical data.
In many cases, this class of bug qualifies as Critical (9.8+ CVSS) under OWASP and NIST CVE scoring systems.
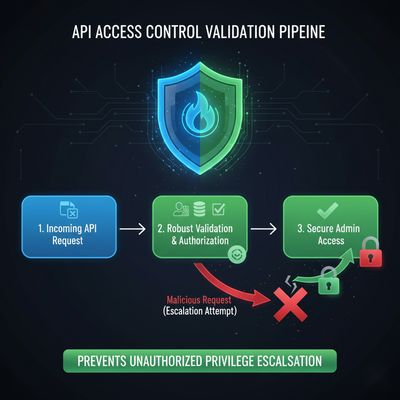
Step 6 - Defensive Perspective: How to Prevent This
Let’s switch hats - from hacker to developer.
Here’s how teams can avoid falling into the same trap.
🔹 Validate Allowed Fields
Only accept known-safe parameters for profile updates. Use whitelists instead of blacklists.
🔹 Enforce Server-Side Role Assignment
User roles should be defined at registration and stored in the database - never modified by user input.
🔹 Implement Authorization Middleware
Every sensitive route must check if the requester has permissions.
🔹 Log Suspicious API Behavior
Unusual requests (e.g., role changes, permission escalations) should trigger alerts or rate limits.
🔹 Conduct Regular API Penetration Tests
BAC issues are among the most common and impactful findings in real-world pentests and bug bounty reports.
Step 7 - Lessons for Bug Hunters
1. Never Ignore the Obvious
Most hunters chase flashy vulnerabilities - but APIs hide gold in plain sight.
2. Observe Every Request and Response
Look for keywords like “role,” “isAdmin,” or “permissions” in JSON data.
3. Test Update Endpoints
PUT and PATCH routes are goldmines. They often accept user input that’s not properly sanitized.
4. Use Burp Suite Wisely
Repeater is your best friend. Modify JSON requests carefully and observe behavior.
5. Don’t Overlook Non-Bounty Targets
Even small or off-scope disclosures can lead to meaningful rewards - or professional gratitude.
6. Keep It Ethical
Never abuse access. Always disclose responsibly and focus on improving security.
Step 8 - How to Practice Privilege Escalation Safely
To gain hands-on experience, you can replicate similar flaws in legal practice environments:
| Platform | Lab | Learning Focus |
|---|---|---|
| PortSwigger Web Security Academy | Broken Access Control Labs | Learn role and object-level authorization flaws. |
| OWASP Juice Shop | Challenge: User → Admin | Realistic practice in privilege escalation. |
| bWAPP / DVWA | Access Control modules | Practice with local vulnerable apps safely. |
| TryHackMe / HackTheBox | Web Challenges | Controlled environments for learning BAC exploits. |
Remember, real-world bug hunting must always respect legal boundaries and scope permissions.
Step 9 - Example Vulnerability Report Template
Title: Privilege Escalation via Role Parameter in API Update Endpoint
Severity: Critical
Impact: User → Admin privilege escalation
Summary:
The /api/v2/users/<id> endpoint allows modification of restricted parameters (role) through client-controlled JSON input. Attackers can escalate privileges and access administrative functionality.
Steps to Reproduce:
-
Log in as a normal user.
-
Send a
PUTrequest to update your profile with the payload: -
Observe response - the role value updates successfully.
-
Access admin-only endpoints or dashboard features.
Impact:
- Full privilege escalation.
- Exposure of sensitive admin-level data.
- Potential for complete compromise of platform integrity.
Recommendations:
- Enforce role validation server-side.
- Restrict modifiable attributes.
- Implement strict authorization middleware.
- Log and monitor privilege changes.
Step 10 - Broader Takeaway: Simplicity Wins
This $130 bounty teaches one powerful truth:
Security isn’t only about complex exploits - it’s about trust boundaries.
Every developer trusts their API “just a bit too much.”
Every hunter ignores one parameter that “probably won’t work.”
That’s where opportunity - and danger - live.
The best hackers question assumptions.
The best developers enforce them.
Step 11 - Motivation for Beginners
If you’re new to bug hunting, let this story motivate you:
- You don’t need advanced tools to find valuable bugs.
- You don’t need deep pockets or huge programs - just curiosity.
- Even a single missing validation can become your first bounty.
Keep learning, keep experimenting, and most importantly, stay ethical.
Your next “too easy” $130 moment might just be one JSON key away.

References
- OWASP Top 10: Broken Access Control
- PortSwigger: Access Control Vulnerabilities
- Mozilla Developer Docs: API Security Best Practices
- OWASP Cheat Sheet: Authorization
Published on herish.me - empowering ethical hackers through real-world stories and actionable security lessons.